Home » Keywords: » The Professor
Items Tagged with 'The Professor'
ARTICLES
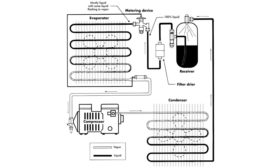
These valuable components keep systems clean but can become restricted themselves
Read More
The Professor: The Perils of Overcharging
Too much refrigerant can cause a number of system issues
Read More
The Professor: More Troubleshooting Tips for Spring Tuneups
Properly diagnosing the symptoms is what sets professional technicians apart
Read More
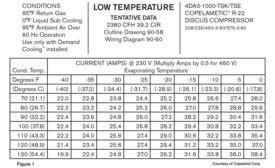
The Professor: Understanding Compressor Amperage Curves
Table-style charts are easy to read and provide valuable information about system function
Read More
The Professor: The Importance of a Refrigeration System’s Operating Pressures
Calculating and analyzing compression ratios can aid system troubleshooting
Read More
The Professor: Calculating Net Temperature Glide
Simple calculations account for system pressure drop
Read More
The Professor: The Correlation Between Refrigerant Blends and Temperature Glide
Composition of the liquid and vapor phases differ due to phase changes
Read More
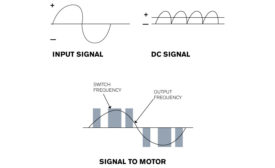
The Professor: Controlling Motor Speed with VFDs
Benefits include improved comfort and energy efficiency
Read More
The Professor: Foiling Frosted Evaporator Coils
Reduced airflow over the coil can cause a multitude of woes
Read More
The Professor: Symptoms of Air in a Refrigeration System
Air May Cause a Reduction in Condensing Surface Area and High Head Pressures
Read More
Copyright ©2024. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing