An open building automation system specification defines the requirements for each aspect of the system.
The workload would become unbearable, which is typically why IT departments pick one platform and stick with it.
Likewise, it is typically recommended to pick one common protocol for an entire building control system infrastructure and stick with it. The costs go down and the maintainability goes up. If there is a specific application or subsystem component that is not available on this standard protocol, or if there is a specific need for using an alternate, this should be justified and a gateway (protocol translator) identified and specified. However, this should be the exception, not the norm.
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
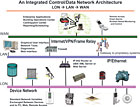
Defining a common system architecture using standard, open methods is important and more appropriate than specifying the buffet style that allows anything to be used. An open building automation system (BAS) provides interoperability where software and hardware from multiple vendors can communicate and coexist without the use of protocol converters and gateways.A good, open BAS specification defines the requirements for each aspect of the system. When defining an open spec, it is important to remember it is more than just the protocol that needs to be specified. There are five elements that also need to be defined:
1. The infrastructure- including the protocol, routers, media type, IT connectivity, etc. All these should be specified based upon open standards, not on one vendor’s specific product. A single system infrastructure provides the benefits of a reduction in construction costs, lower lifecycle and maintenance costs, and an improvement in performance for the whole building.
2. The devices- controllers in the network that produce, consume, or manipulate data and control/monitor the system. In an open system, it is possible to use devices from different vendors because they all conform to a uniform industry standard. This means that the system is not locked into a single supplier allowing the best and most cost-effective equipment to be used. In this way, suppliers are able to concentrate on developing products, which focus on their core competency and do not have to develop a complete system.
Conversely, an integrator who is capable of working with the open protocol will be able to install a complete system selecting the most suitable products from different suppliers. This way, only one integrator is required for the entire system instead of multiple integrators, which can be expensive and cause isolation of the subsystems. An open system also makes upgrading easier and more flexible.
3. Tools- software or network management tools that configure, commission, and maintain the system. The tools on the system need to be able to coexist. Device configuration plug-ins (modules) have been developed to allow the use of any standard network management tool. This allows vendors to configure their devices with an open tool, so users are free to use tools from any vendor they choose.
4. Graphical user interfaces- typically the visualization tools that the user or controls manager uses to obtain a view into the system. User interfaces allow control, monitoring, reporting, alarming, scheduling, and diagnostics. An operator workstation (user interface) affords the means to efficiently and effectively manage operations, as well as display and print a graphical representation of the control network.
A user interface provides the same look and feel for monitoring and control regardless of which vendor’s system or subsystem an operator is viewing. As a result, system operators need only become proficient with one user interface.
5. Enterprise connectivity- the method for connecting the building control network into the data network, known as the LON-LAN-WAN architecture. This ensures that the control system becomes an element of all the data sources available to the enterprise. Open interfaces have been developed to ensure data communication between the LON and LAN is accessible by a vendor. To provide this connectivity, enterprise-level infrastructure devices are needed, and they must be specified as open. Standard routers are used, which means no gateways are required.
OPEN COMMUNICATION
With this information in mind, it is often strongly suggested that contractors limit the main system specification to just one methodology for communication. To ensure a truly open system, all five system elements must be open.Each element must be interoperable, and all training and servicing also must be specified as open; in other words, not locked into one system service provider.
Following this strategy can help reduce costs, improve flexibility and choice of products, provide the option for choosing the best system integrator, and allow for open bidding on both the initial installation and the long-term service contract.
For more information, visit www.lonmark.org.
Publication Date:09/22/2008

Report Abusive Comment